From emergency services to agriculture and food systems, to manufacturing industries, our critical infrastructure systems rely heavily on water. So much so that following a loss of water services, critical infrastructure can begin to degrade rapidly. According to the U.S. Department of Homeland Security after only two hours without water, hospitals can experience up to 66 percent degradation of normal core operations. And after four hours, electric generation plants that depend on water for steam generation, cooling, and fire suppression, can see disruptions in their facility’s systems and operations resulting in as much as 99 percent potential degradation. Without enhancing the resilience of our nation’s water systems, which are intricately intertwined with other critical infrastructure, we leave ourselves vulnerable to potentially catastrophic cascading impacts.
But how do we build resilience in our water systems? What does it even mean to be resilient? In Resiliency: What’s the Buzz?, EFCN introduced the concept of resilience and suggested six basic steps to begin the process of determining your community’s general resiliency. Today we share a framework that helps system operators think through the potentially cascading impacts of threats in order to build more resilient systems.
In March 2016, two UK-based universities teamed up to develop the Safe & SuRe approach of analyzing the reliability, resilience, and sustainability of water management systems. By framing the issue in terms of threats, systems, impacts, and consequences, the Safe & SuRe approach operationalizes an incredibly complex issue.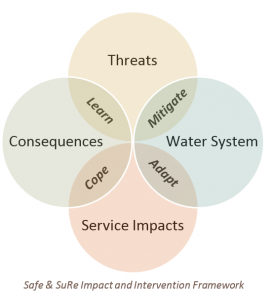
As a systems operator, think about the Threats or events that would result in reduced service. Are they ongoing internal management issues like insufficient investment? Or maybe they might come in the form of a one-time event outside of your control like a tornado.
How can these threats exacerbate your Water System? What are all of the ways your system might fail? An internal structural issue like a pump failure can pose problems for a water system or maybe there is increased water demand because of a rapidly growing population.
What are the Service Impacts as a result of these water system failures? Maybe there is recurrent low supply pressure or maybe there is water discoloration.
What are the social, economic, or environmental Consequences as a result of the service impact? Maybe it is simply an inconvenience, maybe there is loss of agricultural production or increased risk of disease.
Consider the steps you could take to address, respond to, and rebound from these threats. How can you mitigate potential system failures by taking long-term actions to fortify systems against threats? If a system failure does occur, can you adapt and make targeted adjustments to minimize service impacts? If all else fails, what coping strategies or temporary actions can your community take to deal with the consequences of a service impact. And when all is said and done, what are the lessons learned before, during, and after an emergency that can help prepare you for future events?
With an ever-expanding roster of threats such as rapid population changes, extreme weather events, and cyber security attacks, it is important that water systems service operators map out the connections between threats, systems failures, service impacts, and eventually the larger social, economic, and environmental consequences. The Safe & SuRe approach is just one framework for thinking through these issues to enable communities, big or small, to start prioritizing appropriate interventions toward becoming more resilient.
What approach do you take when building your water systems resiliency and what lessons learned can you share with us?

